 Why use tungsten carbide dies? Hardness is the answer.
Why use tungsten carbide dies? Hardness is the answer.
Tungsten carbide is almost three times harder compared with steel and it is of high density than titanium. What this means for companies who use dies is that a tungsten carbide die has a superior wear resistance compared to dies made out of other materials. When dies last longer that is equal to a reduced cost of money in not having the cost of replacing them and in reduced downtime for machinery waiting for new dies to be installed.
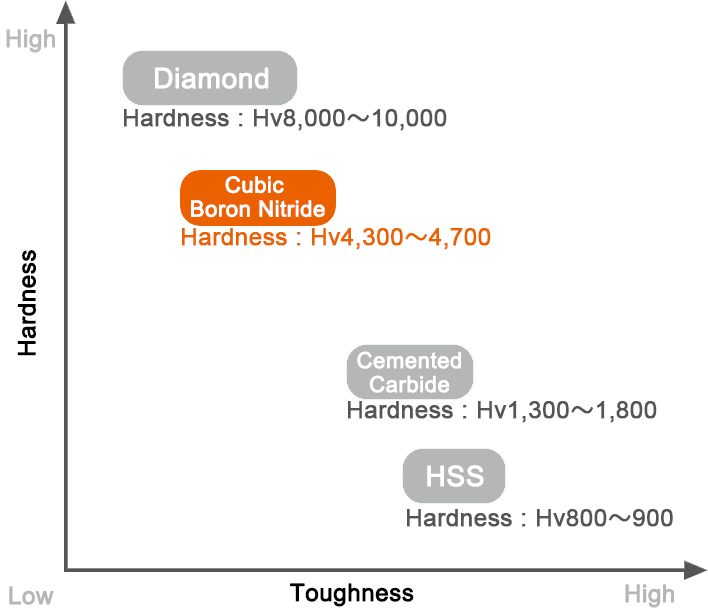
Tungsten carbide has a hardness between 88HRA and 92HRA. Diamond has a hardness rating of 10, however, diamonds aren’t as versatile and are obviously a very expensive die material. In particular, it has the highest hardness and thermal conductivity of any bulk material. Those properties determine the major industrial applications of diamond in cutting and polishing tools.
The tungsten carbide used for die making comes in a wide variety of grades; these different grades have different properties and therefore different applications. The amount of tungsten compared to the amount of carbon in these grades is what makes this difference. By adjusting the tungsten to carbon ratio, carbide dies with better wear properties or greater resistance to impact can be manufactured.
In general, superior hardness combined with the versatility of tungsten carbide results in its wide usage in many industrial applications. Products produced using tungsten carbide dies to include tubing, nails, and nuts. Actually, a list of these products would be very, very long, and that’s where the versatility part of the equation comes in to play.





